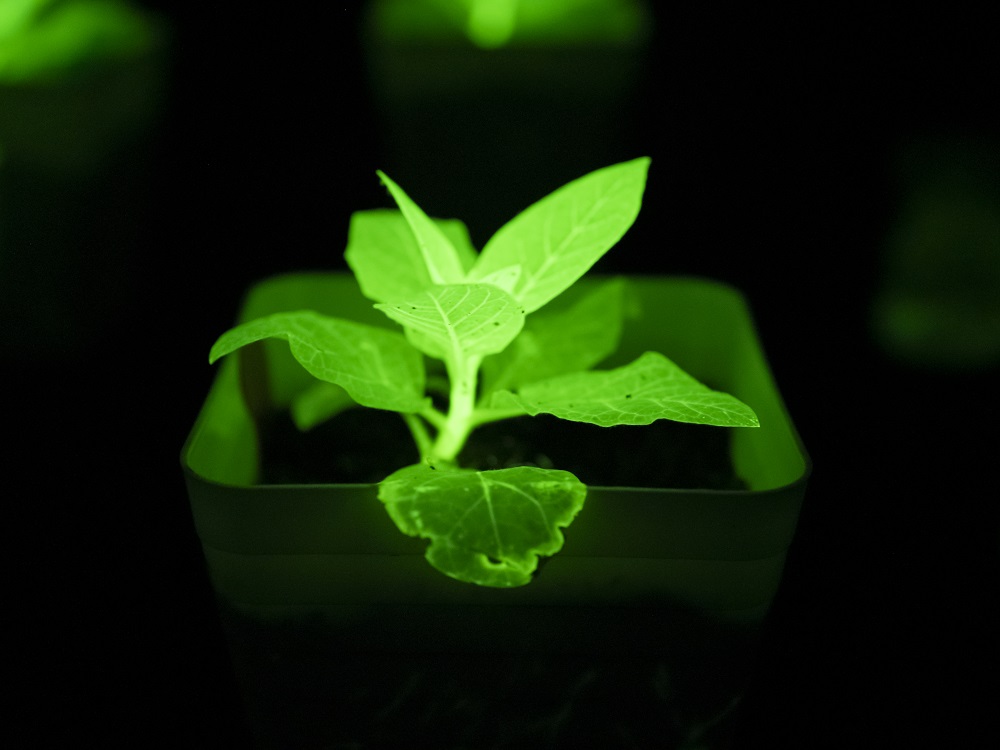
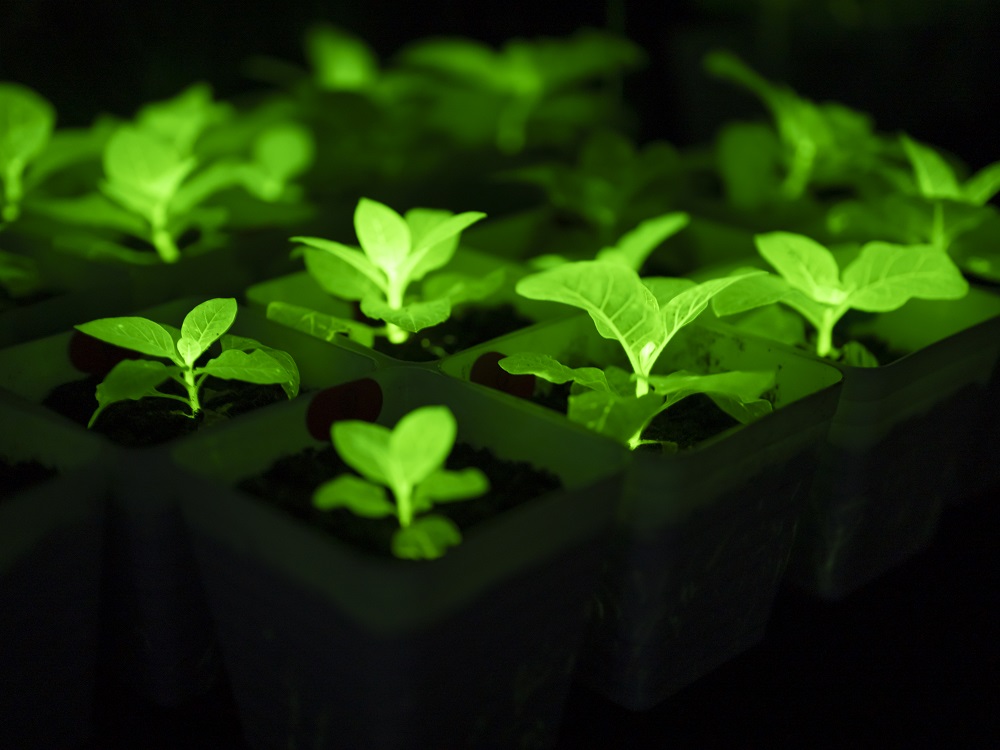
After multiple rounds of laboratory iterations, Shenbi Biotech has achieved a milestone breakthrough in plant luminescence brightness. The core lies in the construction of a multi-dimensional technology system with the world's first dual-gene (TAL tyrosine pathway) pathway patent as the core. It systematically solves the pain points of low luminescence efficiency of traditional technologies from the four major dimensions of pathway efficiency, protein stability, expression localization and enzymatic reaction regulation. The following is an analysis of the core technology:


Core patented pathway: dual-gene regulation to achieve efficiency jump
Traditional technology uses the phenylalanine metabolism pathway, which requires the activation of 5-6 endogenous genes (CM1 gene, PAT gene, ADT2 gene, PAL1 gene, C4H gene, 4CL1 gene) for coordinated expression. There are problems such as long regulatory links, many interactions and interferences, and high product loss. The TAL tyrosine pathway independently developed by Shenbi Biotech uses dual genes to precisely regulate the synthesis of luminescent substrates, bypassing redundant links, and the substrate conversion rate is more than 30 times that of traditional technologies. This pathway has been granted a global exclusive patent and provides core support for high-brightness luminescence.

Anti-degradation small peptide modification: improve the stability of luminescent enzyme
Traditional luminescent enzymes are easily degraded by plant endogenous proteases, resulting in attenuation of luminescent signals. Shenbi Bio introduces an anti-degradation small peptide tag into the coding sequence of the luminescent enzyme. By blocking the recognition site of the degrading enzyme and inhibiting ubiquitination modification, the half-life of the luminescent enzyme is extended from 48 hours to 168 hours, and the steady-state expression is increased by more than 3 times, ensuring that the luminescence brightness remains stable after the enzyme catalyzes the substrate.

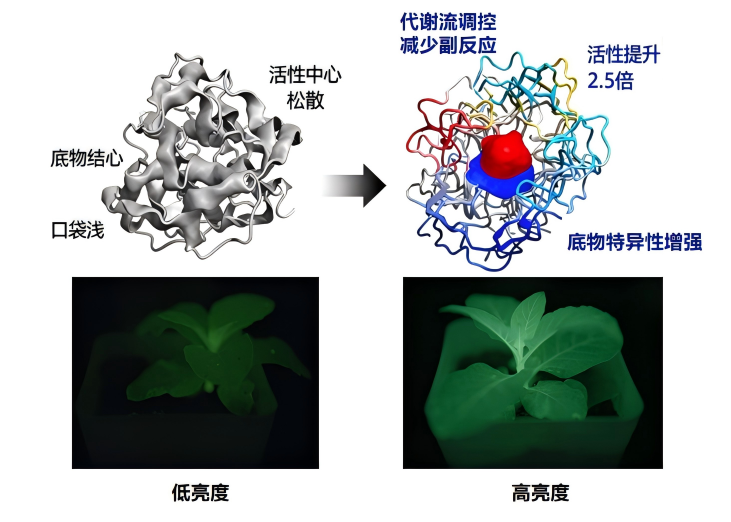
Artificially assisted enzymatic optimization: enhancing catalytic reaction efficiency
The luminescence process is an enzymatic cascade reaction. Traditional technology relies on endogenous enzyme systems and has limitations such as low activity and poor specificity. Shenbi Biotech obtained a mutant with a 2.5-fold increase in enzyme activity through artificial directed evolution, enhanced substrate specific binding ability, combined with metabolic flow regulation to reduce side reactions, and further amplified the luminescence effect.